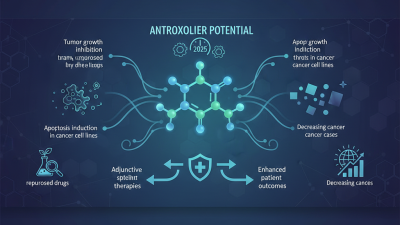
Leave Your Message
The search for effective cancer treatments is ongoing. Traditional therapies have limitations. As we explore new options, the "Mechanism of Nitroxoline in Cancer" emerges as a topic of interest. Nitroxoline, originally used for urinary tract infections, shows potential in oncology. A report from the National Cancer Institute highlighted the promising properties of repurposed drugs like Nitroxoline.
Research indicates that Nitroxoline can inhibit tumor growth. It works by targeting various cellular mechanisms. This includes disrupting DNA synthesis and blocking specific enzymes. Its ability to interfere with cell proliferation opens new avenues for treatment. However, despite encouraging results, the mechanism remains partially understood. Further studies are needed to clarify its full potential.
The efficacy of Nitroxoline in cancer treatment raises numerous questions. Clinical trials are vital to establish its safety and effectiveness. As healthcare evolves, repurposing existing medications may provide quicker solutions. This approach requires a more nuanced understanding of their mechanisms. The journey to uncovering the "Mechanism of Nitroxoline in Cancer" is complex but potentially rewarding, encouraging further exploration in the field.
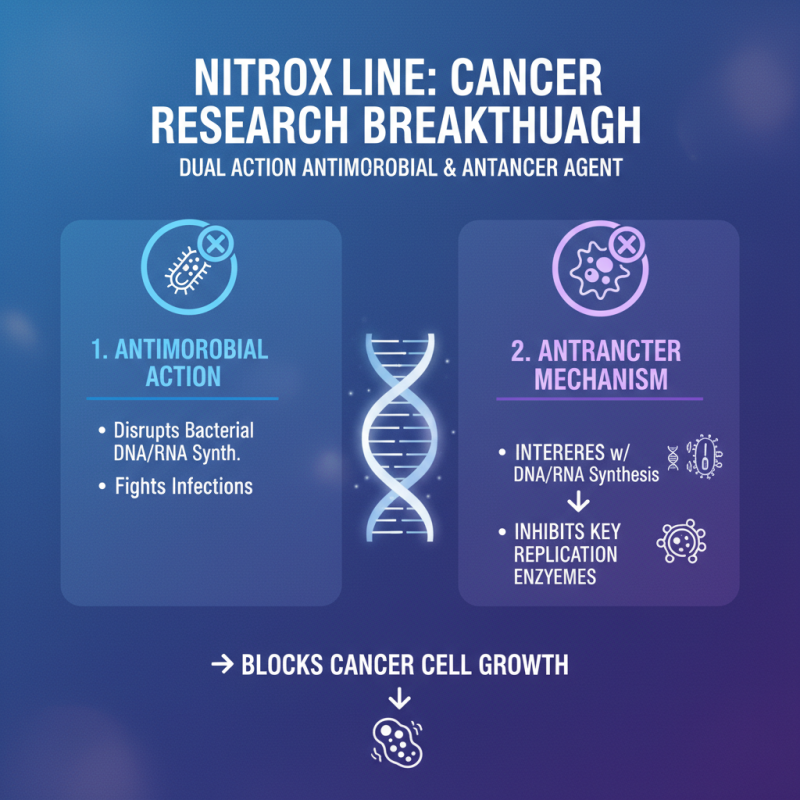
Nitroxoline, a known antimicrobial agent, has garnered attention in cancer research. Its mechanism of action in cancer therapy is intriguing. This compound functions by interfering with DNA and RNA synthesis. By disrupting these essential processes, nitroxoline hinders cancer cell proliferation. Researchers have noted a specific interaction with enzymes that are crucial in DNA replication.
Moreover, nitroxoline exhibits chelating properties. It binds to metal ions, which are vital for various cellular functions. This binding can lead to inhibited tumor growth. Several studies reveal that nitroxoline’s efficacy may vary across different cancer types. Some results are promising, while others show limited effectiveness. This inconsistency invites deeper investigation.
Further exploration into nitroxoline's role is necessary. Potential side effects and optimal dosages remain under scrutiny. Understanding how it interacts with other treatments is vital. The path forward requires collaborative research and open dialogue. Addressing these gaps can help clarify nitroxoline's position in cancer therapy. It’s a complex landscape that demands careful navigation.

Nitroxoline has gained attention in cancer research due to its potential therapeutic effects. Clinical studies show promising results when nitroxoline is applied to various tumors. In one study, patients with bladder cancer exhibited a notable decrease in tumor size. The results were encouraging, suggesting nitroxoline may have a direct impact on tumor growth.
Additionally, researchers discovered that nitroxoline might enhance the effectiveness of standard chemotherapy. This combination could lead to improved outcomes for patients suffering from aggressive cancer types. While these findings are noteworthy, not all studies have shown consistent results. Some trials highlight the need for more extensive research to better understand the drug's full potential.
Reactions vary among different patient populations. Factors such as genetic background can influence responses. More data is essential for tailoring treatments to individual needs. The road to understanding nitroxoline's role in cancer therapy remains complex, highlighting the necessity for ongoing exploration and reflection in this field.
Nitroxoline is gaining attention for its potential in cancer treatment. This compound interacts with various cellular pathways within cancer cells. Its mechanism of action is still being explored, but initial findings show promise. For instance, nitroxoline may inhibit certain enzymes that cancer cells rely on for growth. This interference can disrupt their proliferation.
Research indicates that nitroxoline targets metabolic pathways crucial for cancer cell survival. It appears to affect the expression of genes responsible for cell division. Additionally, nitroxoline may induce apoptosis, a process that leads to programmed cell death. This is particularly important since many cancer treatments aim to eliminate abnormal cell growth.
Despite encouraging discoveries, some questions remain. The specific pathways affected by nitroxoline are not fully understood. Further studies are needed to clarify its role and effectiveness. Researchers are also examining potential side effects. The interaction of nitroxoline with other treatments is another area requiring deeper investigation. Understanding these elements can help optimize its use in cancer therapy.
Nitroxoline is emerging as a potential player in cancer treatment. Unlike traditional chemotherapeutic agents, it targets specific pathways. This unique approach may offer a gentler alternative. Many chemotherapy drugs are known for severe side effects. Patients often experience fatigue, nausea, and hair loss. Nitroxoline presents a different profile. Its mechanism appears to involve inhibiting certain enzymes vital for cancer cell growth.
While research is still ongoing, early studies show promise. Nitroxoline may enhance the effectiveness of existing treatments. It may do this without overwhelming the body’s systems. However, more clinical trials are needed. Some researchers are cautious about its efficacy compared to established drugs. The data vary, and not all patients respond the same way.
Moreover, accessibility could be a concern. Availability may not be uniform across regions. Cost factors also play a role in the drug's adoption in clinical settings. Some healthcare providers may prefer traditional therapies due to established protocols. This raises questions about integration. How can nitroxoline fit into current treatment plans? These are vital discussions as the field of cancer treatment evolves.
Nitroxoline, an antibiotic historically used for urinary tract infections, has emerged as a potential player in cancer therapy. However, using nitroxoline in oncology raises questions about its side effects and limitations. Reports suggest that patients may experience nausea, vomiting, or abdominal pain. These symptoms can overshadow its benefits for some individuals, leaving them to choose between managing pain or facing their illness.
The limitations of nitroxoline as a cancer treatment stem from its scope of action. While it shows promise against certain cancer cells, it is not universally effective. Researchers are still determining optimal dosages and treatment durations. This uncertainty may lead to inconsistent results in clinical settings. Furthermore, any potential interactions with other cancer medications remain unclear. Such factors can complicate treatment plans, often requiring more comprehensive patient monitoring.
Patient safety is paramount in oncology. Although nitroxoline is relatively well-tolerated, it is not devoid of risks. Some patients experience allergic reactions or other unexpected effects. The challenge lies in balancing its potential benefits with the side effects. Ongoing studies may help clarify its role but also highlight the need for caution when integrating it into cancer treatment regimens.