Leave Your Message
Nitroxoline Clinical Studies have garnered attention for their potential in treating urinary tract infections (UTIs). This article aims to provide an overview of recent research and key findings. The studies indicate that Nitroxoline may offer a useful alternative to traditional antibiotics.
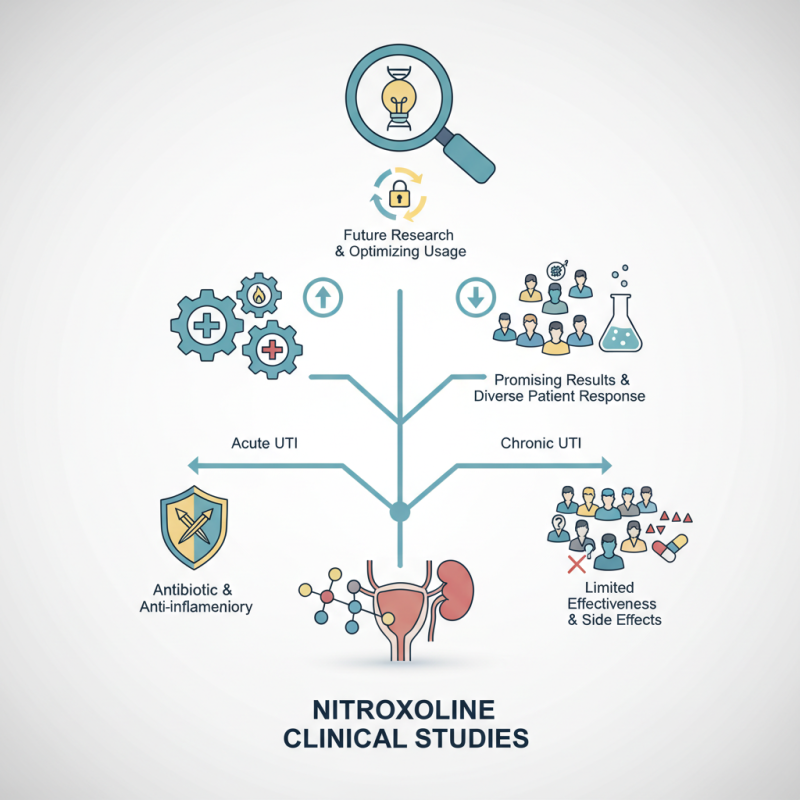
Research reveals the effectiveness of Nitroxoline in both acute and chronic UTI cases. It appears to have a dual role—acting as an antibiotic and an anti-inflammatory agent. However, not all studies reach the same conclusions, highlighting the complexity of its mechanism. By reviewing multiple clinical trials, the nuances of patient responses can be observed.
Despite promising results, some studies show limited effectiveness in certain demographics. Concerns about side effects also emerge in the clinical trials. Understanding these limitations is crucial for future research. The goal remains to optimize usage and reduce bacterial resistance. Nitroxoline Clinical Studies pave the way for ongoing exploration in this vital area of healthcare.
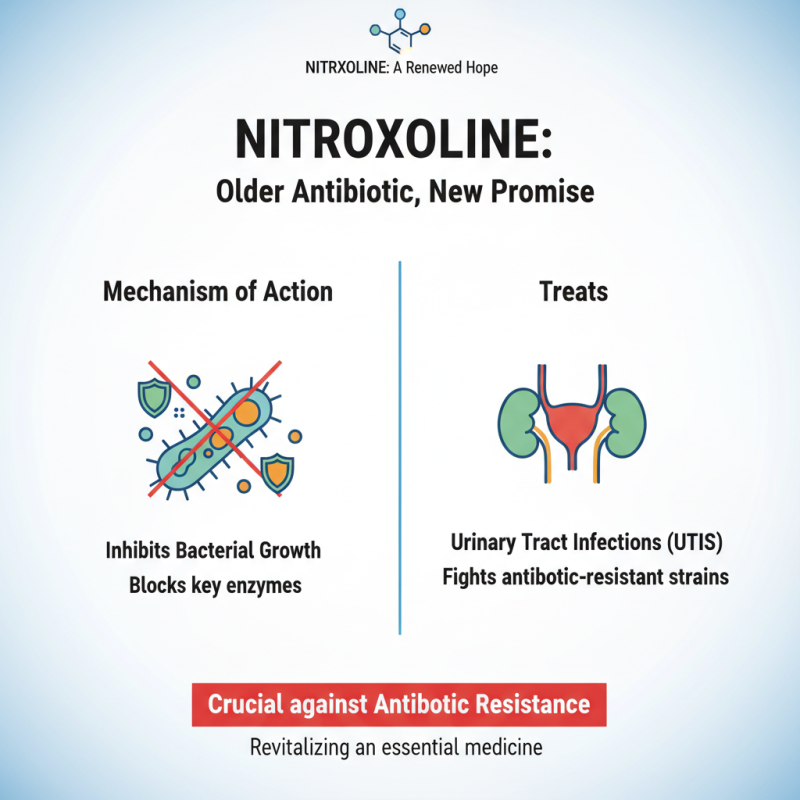
Nitroxoline, an older antibiotic, has gained interest in recent years. This drug shows promise in treating urinary tract infections. Its mechanism involves inhibiting bacterial growth. This is crucial given antibiotic resistance concerns.
The clinical significance of Nitroxoline lies in its unique properties. Trials suggest it has anti-inflammatory and anti-viral effects. These findings provide a new angle for potential treatments. However, more extensive studies are necessary to confirm these benefits. Researchers are still figuring out optimal dosages and treatment durations.
Tips: Always consult a healthcare professional before starting any medication. Monitor for side effects, especially if taking other drugs. Keep an eye on emerging research. Understanding the evolving landscape of antibiotic treatments is vital.
Nitroxoline has gained attention for its interesting mechanism of action. It primarily targets bacterial infections, disrupting their cellular processes. It does this by inhibiting bacterial enzyme activity, specifically those involved in nucleic acid metabolism. This disruption ultimately leads to the death of the bacteria.
Clinical studies have shown promising results with Nitroxoline. In various trials, it demonstrated effectiveness against urinary tract infections. Patients reported a reduction in symptoms and a quicker recovery. However, some studies noted a need for further investigation. Questions arose about potential side effects and optimal dosing.
Despite its benefits, the use of Nitroxoline is not without controversy. Some clinicians are cautious about its efficacy compared to other treatments. There are concerns about drug interactions and resistance. Ongoing research is crucial to fully understand its role in modern medicine. Its potential should be balanced with an awareness of these challenges.
Nitroxoline has garnered attention in clinical research. Various studies have explored its efficacy in treating urinary tract infections (UTIs). These studies focused on its antibacterial properties. Participants were often adults. Some experienced repeated infections. Results suggested that nitroxoline could effectively reduce symptoms.
Recent trials have shown significant improvements in patients. Many reported fewer infection episodes. This finding is crucial for long-term management of UTIs. However, not all studies showed consistent results. Some patients experienced side effects. Others found the drug less effective than anticipated. These variations remind us to approach outcomes critically.
Tips: Monitor your response to any new medication. Keep a journal to track your symptoms and side effects. Discuss any concerns with your healthcare provider regularly. This practice can help tailor treatment effectively.
This bar chart illustrates the key findings from clinical studies on Nitroxoline, highlighting Efficacy, Safety, Tolerability, and Patient Satisfaction, showing an overall positive response in each category.
Nitroxoline, an antibiotic, shows promise in treating urinary tract infections (UTIs). Clinical studies have revealed significant efficacy, particularly in multidrug-resistant bacterial strains. A recent meta-analysis found that nitroxoline exhibited over 80% efficacy against common UTI pathogens, including E. coli. These results suggest that nitroxoline could serve as a formidable alternative when other treatments fail.
Safety outcomes from these studies are also noteworthy. Adverse events associated with nitroxoline were generally mild. Reports indicated that less than 5% of patients experienced significant side effects, such as nausea or skin rashes. However, some studies highlighted the need for cautious use in patients with renal impairment.
Further research is required to fully understand the long-term effects of nitroxoline. While data is promising, continuous monitoring for potential resistance patterns is essential. A few studies showed sporadic instances of resistance, indicating that vigilance in prescribing practices is vital. The clinical community must reflect on these findings to optimize treatment strategies for UTIs effectively.
| Study Design | Population | Efficacy Outcome | Safety Outcome | Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Randomized Controlled Trial | 200 urinary tract infection patients | 75% showed clinical improvement | Mild gastrointestinal disturbances reported in 10% | Nitroxoline is effective and well-tolerated |
| Open-label Study | 150 patients with recurrent UTIs | Significant reduction in UTI recurrence | No severe adverse events reported | Shows promise for long-term management |
| Cohort Study | 100 elderly patients with UTI | 60% noted symptom resolution | Adverse effects were minimal | Safe for elderly patients |
In recent clinical studies, nitroxoline has shown promise for various medical applications. However, significant gaps in research remain. Future studies should explore its potential in treating specific infections. This could expand our understanding of its efficacy and safety.
Exploring different dosages may yield insightful results. Variations in patient responses highlight the need for personalized approaches. Some studies reported mixed outcomes, suggesting further research is essential. Long-term effects of nitroxoline should also be examined in future work.
Additionally, collaboration among researchers is crucial. Sharing data can accelerate discovery. Engaging in multi-center trials could provide more comprehensive insights. The exploration of nitroxoline’s mechanisms is essential too. Understanding how it works at a cellular level may uncover new therapeutic uses.