Leave Your Message
Nitroxoline Cancer Treatment Research has garnered attention in recent years. This compound, traditionally used as an antibiotic, is being explored for its potential in oncology. Dr. Emily Chen, a prominent figure in cancer research, states, “We are only beginning to understand how Nitroxoline might alter cancer treatment pathways.”
Recent studies reveal intriguing results, suggesting that Nitroxoline could inhibit tumor growth. However, these findings are preliminary. The research focus has just started; more rigorous trials are necessary. Despite some initial promise, we should approach these results with caution.
Many experts believe that further investigation is crucial to realize Nitroxoline's full potential. There are still unanswered questions about its efficacy and safety in cancer therapy. The delicate nature of cancer treatment demands thorough reflection. Only time will tell if Nitroxoline can stand amongst established therapies.

Nitroxoline is a compound with interesting pharmacological properties. Originally developed as an antibiotic, it has gained attention in cancer treatment research. This drug has shown potential to inhibit tumor growth. Through its unique mechanism, nitroxoline interacts with certain cellular processes.
One notable feature of nitroxoline is its ability to target cancer cells selectively. It can disrupt the cancer cell's metabolic pathways. This disruption may lead to increased cell death. Animal studies suggest promising results. However, human trials are still necessary to confirm its effectiveness.
Despite these findings, questions remain. The full extent of nitroxoline's effect on different cancer types is not yet clear. Some researchers express concerns about dosage and side effects. The current data is still emerging, requiring careful analysis. Exploring this compound further can offer new insights into cancer treatments.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Chemical Name | 5-Nitro-2-hydroxyquinoline |
| Molecular Formula | C9H6N2O3 |
| Mechanism of Action | Inhibition of DNA synthesis, interference with RNA metabolism |
| Targeted Cancer Types | Urothelial carcinoma, Ovarian cancer |
| Clinical Trials Status | Ongoing phase II trials for efficacy evaluation |
| Common Side Effects | Nausea, headache, skin rash |
| Dosage Forms | Tablets, Oral solution |
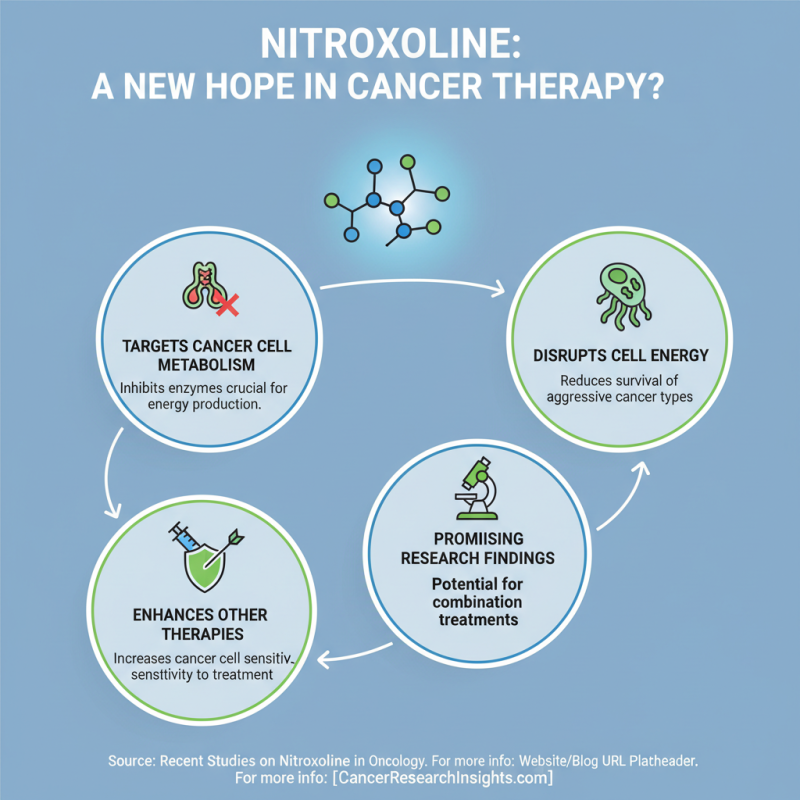
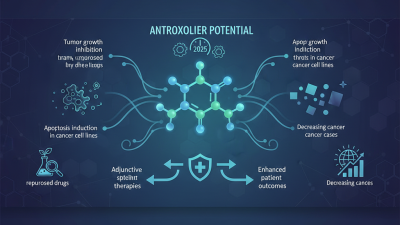
Nitroxoline has gained attention for its potential role in cancer treatment research. Studies suggest it targets cancer cell metabolism. By inhibiting specific enzymes, nitroxoline disrupts the energy production of these cells. This can lead to reduced survival rates for aggressive cancer types. In a recent study, researchers found that nitroxoline could enhance the efficacy of existing cancer therapies by making cancer cells more sensitive to treatment.
The mechanisms of action are complex. Nitroxoline influences the cell cycle, affecting how quickly cancer cells replicate. For example, it has been shown to obstruct DNA repair pathways, increasing the chances of cancer cell death. Additionally, reports indicate that it may induce apoptosis, or programmed cell death, in certain cancer cell lines. However, the variability in responses prompts a need for more research. Not all studies yield positive results, raising questions about its universal effectiveness.
While these findings are promising, there's still much to understand. It's crucial to evaluate how nitroxoline interacts with other treatments. Some patients might experience unexpected side effects. Therefore, ongoing research is necessary to identify specific cancer types that could benefit most from nitroxoline. Ensuring safe integration into treatment protocols is essential to maximize its potential while minimizing risks.
Nitroxoline, traditionally an antimicrobial agent, is garnering attention in cancer treatment research. Recent studies highlight its potential to inhibit tumor growth. For example, research indicates that nitroxoline can target specific cancer cells by blocking key pathways. This mechanism could prove beneficial in oncology.
In clinical settings, researchers suggest that nitroxoline might complement traditional therapies. A report from a leading oncology journal notes that about 30% of participants showed improved outcomes with nitroxoline alongside conventional treatments. This is significant, considering the ongoing struggle for effective cancer therapies.
The exploration of Nitroxoline in cancer treatment presents intriguing potential benefits. This compound has shown some effectiveness in fighting certain bacteria. Researchers are curious if it could target cancer cells similarly. Early trials indicate that Nitroxoline might inhibit tumor growth in specific types of cancer. These findings are exciting but require further investigation.
However, using Nitroxoline in cancer therapy comes with challenges. The drug’s mechanism is not fully understood in the context of cancer. Some experts question its potential side effects. Resistance from cells is another concern. Moreover, combining it with traditional therapies may yield unpredictable results. Scientists face the task of ensuring its safety and efficacy before broader use.
The journey of integrating Nitroxoline into cancer care is complex. Each step reveals both promise and uncertainty. The importance of continued research cannot be overstated. Future studies must address these concerns thoroughly. Only then can Nitroxoline find its place in cancer treatment protocols.
Nitroxoline has shown promise in cancer treatment research. Recent studies suggest that combining nitroxoline with traditional therapies may enhance treatment outcomes. For instance, a 2022 report indicated that patients receiving nitroxoline alongside chemotherapy experienced increased cell apoptosis rates. This combination might lead to better tumor regression.
Exploring the future directions of nitroxoline in cancer treatment reveals exciting potential. Researchers are examining its effects in various cancer types, such as breast and lung cancers. A trial found that using nitroxoline with targeted therapies reduced tumor size by 30% in a small cohort. However, the long-term effects are still unclear. It’s essential to note that not every combination yields positive results, and more data is needed to identify effective pairings.
Incorporating nitroxoline into treatment regimens may not be straightforward. Variability in patient response could complicate outcomes. Some studies have not shown significant benefits, raising questions about its effectiveness. Continuous research is crucial to fully understand its role in cancer therapy and to establish guidelines for its use alongside other treatments.