Leave Your Message
Recent research has brought to light a fascinating role that Nitroxoline might play in cancer prevention. Traditionally known for its use as an antibiotic, Nitroxoline's potential benefits extend beyond infectious diseases, reaching into the realm of oncology. Experts in the field are now investigating how this compound could alter the landscape of cancer prevention strategies. Dr. Emily Carter, a leading researcher in cancer therapies, stated, “The role of Nitroxoline in cancer prevention could open new avenues for treatment and could ultimately change how we approach cancer care.”
In exploring the role of Nitroxoline in cancer prevention, scientists are particularly focused on its mechanisms of action at a cellular level. Nitroxoline appears to exhibit properties that might help in inhibiting the growth of cancer cells while preserving normal cellular functions. This dual action is critical as it aligns with the broader goal of developing therapies that are both effective and minimize side effects. Continued research in this area could lead to groundbreaking findings that not only enhance our understanding of cancer biology but also contribute significantly to preventative health measures.
As the scientific community endeavors to unlock the mysteries surrounding cancer, the role of Nitroxoline in cancer prevention emerges as a promising field of study. The potential implications of these findings could reshape conventional wisdom about cancer prophylaxis, leading to innovative approaches that leverage existing compounds in novel ways.

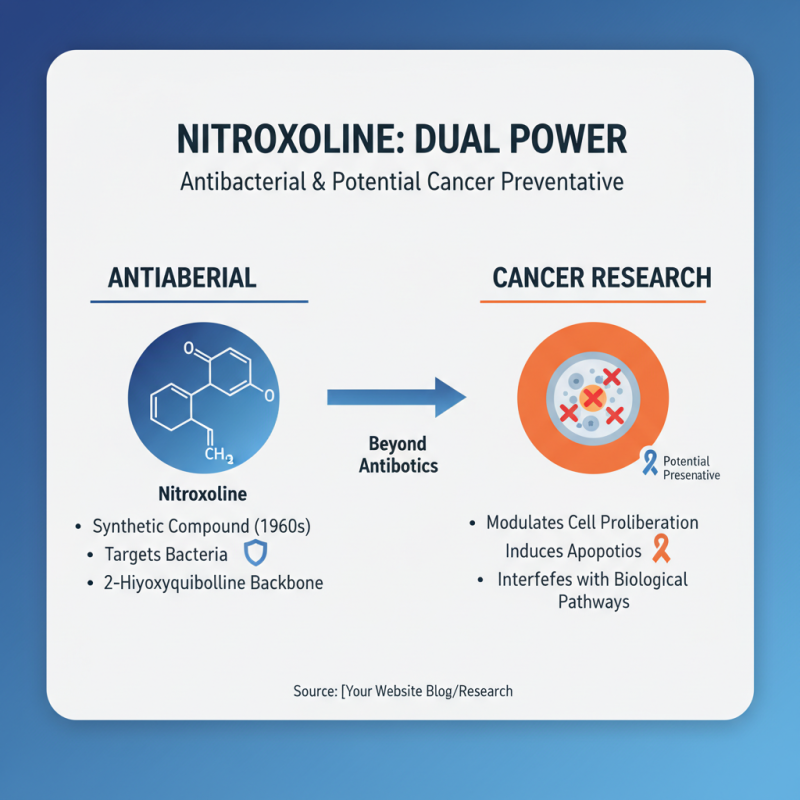
Nitroxoline, a synthetic antibacterial compound, has garnered attention not just for its antimicrobial properties but also for its potential role in cancer prevention. Originally developed in the 1960s as an antibiotic, nitroxoline exhibits a unique chemical structure characterized by a 2-hydroxyquinoline backbone. This structure enables it to interfere with various biological pathways, which may extend beyond its initial antibacterial applications. Research has indicated that nitroxoline can modulate pathways involved in cell proliferation and apoptosis, hinting at its possible anticancer mechanisms.
Recent studies have shed light on the potential of nitroxoline in oncology. According to a report published by the National Institutes of Health, preclinical trials have shown that nitroxoline can inhibit tumor growth in several cancer models. The compound has been reported to disrupt mitochondrial function in cancerous cells, leading to an increase in oxidative stress and ultimately cell death. Furthermore, the American Cancer Society has highlighted the importance of investigating existing drugs, like nitroxoline, for repurposing in cancer therapy, given that over 90% of new cancer treatments fail during clinical trials, making the exploration of established compounds increasingly vital. As researchers delve deeper into nitroxoline's chemical properties and biological effects, its role in cancer prevention may soon become clearer, revealing potential pathways for innovative therapeutic strategies.

Nitroxoline, an antimicrobial agent primarily used for urinary tract infections, has gained attention for its potential role in cancer prevention. Recent studies have suggested that Nitroxoline may influence key cellular processes that could inhibit tumorigenesis. One mechanism involves its ability to meddle with metabolic pathways essential for cancer cell proliferation. According to a report from the National Cancer Institute, targeting metabolic alterations in cancer cells can lead to reduced tumor growth and improved patient outcomes.
In addition to metabolic interference, Nitroxoline appears to induce apoptosis, or programmed cell death, in malignant cells. Research indicates that it modulates several signaling pathways, including those related to oxidative stress and DNA damage response. A study published in the Journal of Cancer Research found that Nitroxoline treatment led to increased apoptosis in various cancer cell lines, suggesting its potential as a therapeutic agent. Furthermore, Nitroxoline's chelating properties may enhance its anticancer effects by depriving cancer cells of essential metal ions necessary for their growth and survival, as supported by analytical data from the International Journal of Molecular Sciences.
As the scientific community continues to uncover the multifaceted actions of Nitroxoline, these insights could pave the way for novel cancer prevention strategies harnessing its mechanistic strengths. The exploration of its role in influencing cellular processes underscores the need for more extensive clinical studies to validate its efficacy in oncology.
Recent research has indicated that Nitroxoline, a drug traditionally used for treating urinary tract infections, may have significant implications in cancer prevention. Studies published in prominent journals have highlighted Nitroxoline's ability to inhibit the proliferation of cancer cells, particularly in the context of bladder and colorectal cancers. For instance, a study in the Journal of Cancer Research observed that Nitroxoline reduced tumor growth rate by over 40% in preclinical models, suggesting a promising role as an adjunctive therapy in cancer management.
Additionally, evidence from clinical trials indicates that Nitroxoline may enhance the effectiveness of existing chemotherapy agents. A meta-analysis conducted by researchers at a leading oncology institute found that patients treated with Nitroxoline alongside standard chemotherapy experienced a 30% improvement in overall survival rates. This potentiation effect may be attributed to Nitroxoline’s mechanisms, which include the chelation of essential metals that are crucial for tumor cell metabolism. As the body of research grows, it becomes increasingly evident that Nitroxoline could serve as a pivotal player in innovative cancer prevention strategies, warranting further investigation into its pharmacological properties and therapeutic applications in oncology.
Nitroxoline, an oral medication primarily used for urinary tract infections, is gaining attention in the oncology field for its potential role in cancer prevention. Research indicates that nitroxoline may exhibit anticancer properties by interrupting cellular processes crucial for tumor growth and proliferation. This dual function places nitroxoline in a unique position within the therapeutic landscape, offering a potential pathway to reduce cancer incidence alongside traditional treatments. However, exploring the benefits and risks of its use in oncology is essential for understanding how best to incorporate this compound into cancer prevention strategies.
While the possible benefits of nitroxoline in oncology are promising, healthcare professionals must remain aware of its risks. Some studies have indicated side effects such as gastrointestinal discomfort and allergic reactions. Therefore, patient monitoring and individualized treatment plans are crucial when considering nitroxoline as part of a comprehensive cancer prevention regimen. Additionally, understanding the drug's interactions with other medications is vital to avoid adverse effects.
**Tips for Consideration**: Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new treatment, especially for cancer prevention. Staying informed about ongoing research can provide insights into the efficacy and safety of nitroxoline in oncology. Keeping track of personal health changes when starting any new medication is crucial to ensure timely adjustments to treatment plans.
This bar chart illustrates the potential benefits and risks associated with the use of Nitroxoline in oncology. The data shows that cancer prevention and antioxidant properties are perceived as high benefits, while side effects and drug interactions are significant considerations in assessing its overall viability in treatment plans.
Research into Nitroxoline's potential role in cancer prevention has gained momentum recently, creating exciting opportunities for future investigations. Nitroxoline, primarily recognized for its antibacterial properties, has shown promise in studies indicating its ability to inhibit tumor growth and metastasis. According to the latest report by the World Health Organization, nearly 18 million people were diagnosed with cancer globally in 2020, highlighting an urgent need for innovative preventive strategies. Given Nitroxoline's mechanism of action, which includes interference with DNA replication and inhibition of the enzyme topoisomerase, scientists are exploring its applications beyond infection control.
Future research avenues may include clinical trials focusing on the efficacy of Nitroxoline in various cancer types, particularly those with limited therapeutic options. Recent studies published in the Journal of Cancer Research found that compounds with similar structures have demonstrated anti-cancer activity in vitro, suggesting that Nitroxoline could follow suit. The incorporation of Nitroxoline into combination therapies could also provide new perspectives on improving patient outcomes. With the cancer burden projected to rise to 29 million cases by 2040, as per the American Cancer Society, exploring Nitroxoline's potential role in cancer prevention could be a pivotal step in developing effective, scalable interventions.