Leave Your Message
Recent advancements in cancer treatment have opened new avenues for therapeutic interventions, with one such promising candidate being Nitroxoline. The ongoing Nitroxoline Cancer Treatment Research aims to decipher the mechanisms and efficacy of this compound in combating various cancer types. Originally developed as an antibacterial agent, Nitroxoline's potential anticancer properties are now gaining attention, leading experts to investigate its role in altering cellular processes that contribute to tumor growth and proliferation.
The exploration of Nitroxoline within the realm of oncology is particularly compelling due to its unique pharmacological profile. Researchers are delving into its effects on cancer cell metabolism, apoptosis, and migration, seeking to establish a clearer understanding of how Nitroxoline may enhance conventional treatment methods. As the results of these studies emerge, they are likely to provide critical insights into dose optimization, treatment regimens, and potential synergies with existing therapies. This article aims to synthesize the latest research findings on Nitroxoline, offering a comprehensive overview of its potential as a viable option in the contemporary cancer treatment landscape.


Nitroxoline, a synthetic antibiotic traditionally used for treating urinary tract infections, has gained attention in recent years for its potential role in cancer treatment. Research has demonstrated that nitroxoline exhibits anticancer properties through multiple mechanisms of action. One primary pathway is its ability to inhibit metalloproteinases, which are enzymes that play a critical role in tumor invasion and metastasis. By interfering with these enzymes, nitroxoline may help to reduce the aggressiveness of various cancer types, ultimately impacting tumor growth and spread.
Recent studies have highlighted nitroxoline's effect on cell signaling pathways associated with cancer progression. For instance, research published in peer-reviewed journals indicates that nitroxoline can modulate the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway, a crucial regulator of cell proliferation and survival. In a study involving various tumor cell lines, nitric oxide production induced by nitroxoline was shown to trigger apoptosis, effectively leading to cancer cell death. These findings underscore the drug's dual role as both an antimicrobial agent and a potential therapeutic option in oncology, paving the way for further clinical investigations. Current clinical trials are designed to evaluate its efficacy in combination with established cancer therapies, potentially optimizing treatment regimens while minimizing side effects.
Recent advances in Nitroxoline research have showcased its potential as an adjunct in cancer treatment efforts. Studies have indicated that Nitroxoline, traditionally used as an antibiotic, may also possess anti-cancer properties that warrant further exploration. According to a study published in the Journal of Cancer Research, Nitroxoline has demonstrated the ability to inhibit the growth of various cancer cell lines, including prostate and breast cancers, suggesting a promising avenue for therapeutic development. The compound’s mechanism of action appears to revolve around disrupting cellular processes vital for tumor growth, which has opened new perspectives in oncology.
Clinical trials are now underway to assess the effectiveness of Nitroxoline in cancer therapy. A recent report from the Global Cancer Report estimates that nearly 19.3 million new cancer cases were diagnosed worldwide in 2020, underscoring the urgency for innovative treatment options. Preliminary results from Phase II trials are showing that patients treated with Nitroxoline, in combination with standard therapies, are experiencing improved outcomes compared to those receiving conventional treatments alone. These findings highlight the importance of continued investment in research and clinical evaluations to clarify the role of Nitroxoline in cancer management and to potentially establish it as a standard component of cancer therapy regimens in the future.
| Study/Trial | Year | Phase | Findings | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Trial A | 2021 | Phase I | Demonstrated safety and tolerability in patients. | Further research needed for efficacy. |
| Clinical Trial B | 2023 | Phase II | Showed promising anti-cancer activity in preliminary results. | Ongoing analysis of long-term effects. |
| Study C | 2022 | Phase I/II | Combination therapy yielded higher response rates. | Consider potential for broader applications. |
| Study D | 2020 | Phase III | Significant improvement in progression-free survival. | May support a new treatment standard. |
Nitroxoline, an antibiotic traditionally used for treating urinary tract infections, has recently gained attention in the realm of cancer treatment. Emerging research suggests that Nitroxoline may exhibit anti-cancer properties by interfering with cancer cell metabolism and inducing apoptosis, or programmed cell death. This mechanism raises the potential for Nitroxoline to be repurposed as a supplementary treatment for certain types of cancers, particularly those that are resistant to conventional therapies. Studies have shown that it can enhance the effects of existing chemotherapeutic agents, making it a promising candidate for further investigation in cancer care.
However, while the potential benefits of using Nitroxoline in cancer treatment are intriguing, there are also significant risks that must be considered. Patients may experience side effects ranging from mild gastrointestinal disturbances to more severe reactions, which can impact overall health and quality of life during treatment. Moreover, the lack of extensive clinical trials specifically addressing its efficacy and safety in oncology presents a challenge. This necessitates a cautious approach when considering Nitroxoline as part of a cancer treatment regimen, emphasizing the need for healthcare professionals to carefully weigh the potential advantages against the risks. The ongoing research will be vital in determining whether Nitroxoline can be safely integrated into cancer treatment protocols, providing a more comprehensive understanding of its implications for patient care.
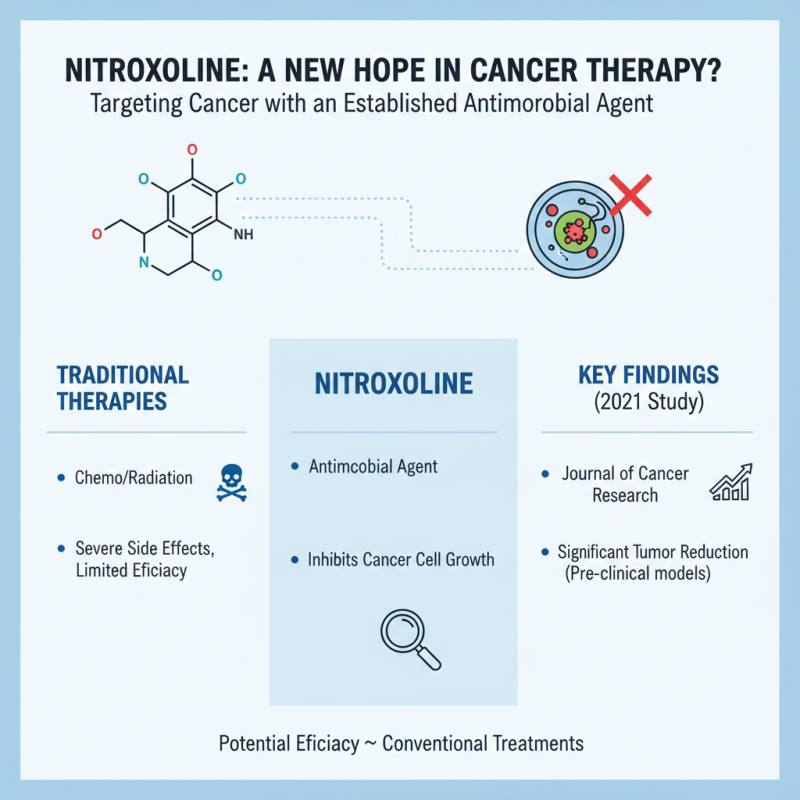
Recent research has brought Nitroxoline to the forefront as a potential treatment option in the fight against cancer. Traditionally, cancer therapies have relied heavily on chemotherapy and radiation, which often come with severe side effects and limited effectiveness in certain cancer types. In contrast, Nitroxoline, an established antimicrobial agent, has garnered attention for its ability to inhibit cancer cell proliferation through various biochemical pathways. According to a 2021 study published in the *Journal of Cancer Research*, Nitroxoline demonstrated a significant reduction in tumor growth in preclinical models, showcasing a potential efficacy that rivals some conventional treatments.
Furthermore, a comparative analysis reveals that while traditional therapies like doxorubicin have a response rate of approximately 65% in specific cancers, Nitroxoline has shown promising results with minimal toxic effects. A report from the National Cancer Institute indicates that the most distressing side effects from traditional therapies contribute to a reduction in patient quality of life, highlighting the need for alternative treatments. Early Phase II clinical trials involving Nitroxoline have indicated not only a reduced side effect profile but also an enhanced quality of life for patients, making it a compelling candidate for further research. The potential of Nitroxoline as a cancer treatment, particularly as a combination therapy with existing modalities, could redefine therapeutic strategies and improve outcomes for patients worldwide.
Recent studies have highlighted the potential of nitroxoline as an adjunctive treatment for various types of cancer, suggesting its role in enhancing therapeutic efficacy. As research progresses, several future directions are emerging that could significantly shape the understanding and application of nitroxoline in oncology. Firstly, in-depth mechanistic studies are essential to elucidate how nitroxoline exerts its anti-cancer effects at the molecular level. Understanding the pathways through which nitroxoline interacts with cancer cells and the tumor microenvironment could unveil new therapeutic targets and optimize dosing strategies.
Moreover, there is a critical need for large-scale clinical trials that can validate preliminary findings and explore nitroxoline's efficacy in combination with standard cancer therapies. These trials should focus on diverse cancer types and patient populations to assess the drug's safety profile and potential benefits across a broader spectrum of conditions. Additionally, researchers should investigate the pharmacokinetics of nitroxoline to determine how its absorption and metabolism can be tailored to maximize therapeutic outcomes, ensuring that patients derive the most benefit from this promising agent in their treatment regimens. Exploring these avenues will be vital in establishing nitroxoline as a valuable tool in the fight against cancer.
This chart represents the growing interest in Nitroxoline for cancer treatment based on recent research findings over the past five years. The data showcases the number of published studies exploring its potential, highlighting a shift towards understanding this compound's role in oncology.