Leave Your Message
Nitroxoline as an anticancer agent has emerged as a topic of growing interest. This compound, originally used as an antibiotic, shows potential in cancer treatment. Research indicates that Nitroxoline can target cancer cells effectively. It might help in slowing down tumor growth.
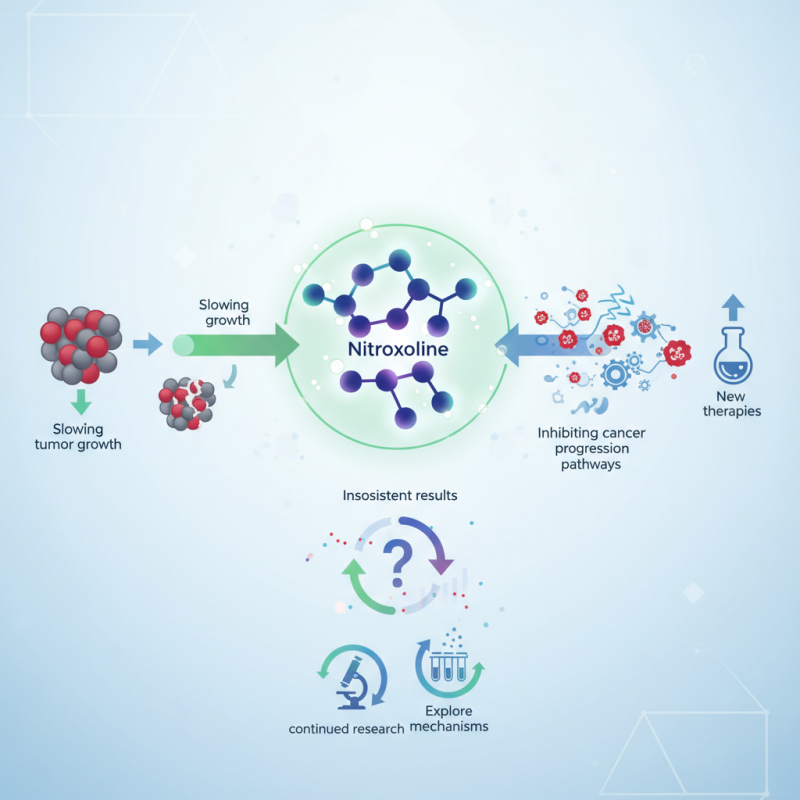
Moreover, studies suggest that Nitroxoline possesses unique properties. For instance, it can inhibit pathways involved in cancer progression. This creates exciting possibilities for developing new therapies. However, the path is not entirely clear. Some studies yield inconsistent results, raising questions about its efficacy.
It is crucial to explore the mechanisms behind Nitroxoline as an anticancer agent. This understanding may lead to improved treatments. Continued research is necessary to establish clear guidelines and optimize its use in oncology. Balancing hope with caution is essential in this evolving field.
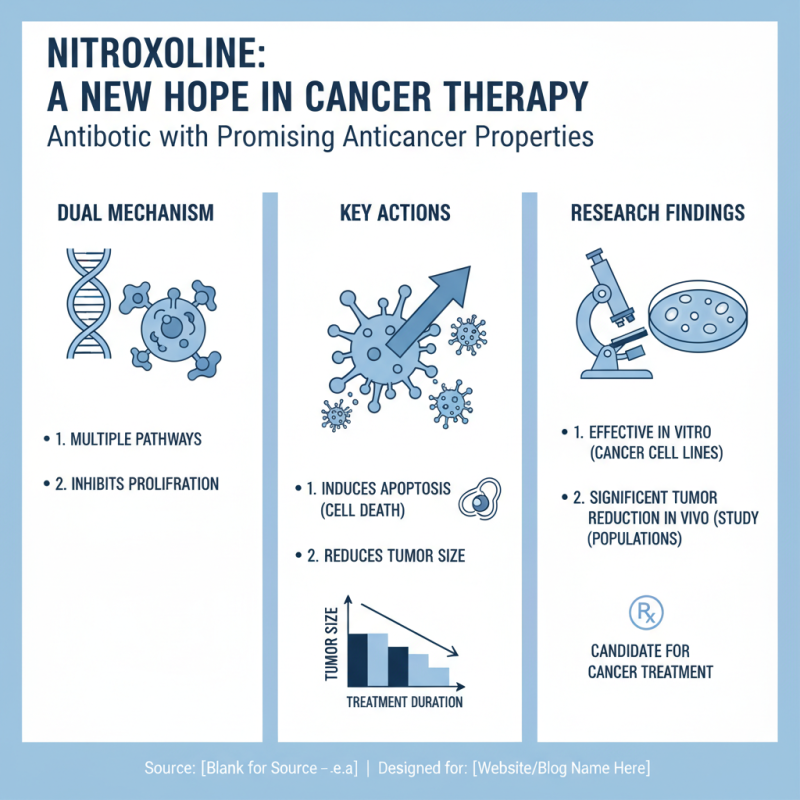
Nitroxoline, an antibiotic, shows promise as an anticancer agent. Its mechanism of action involves multiple pathways, making it a candidate for cancer treatment. Research indicates that Nitroxoline can inhibit certain cancer cell proliferation. For instance, a study found that it induces apoptosis in various cancer cell lines. Data shows a significant reduction in tumor size for tested populations.
Inhibiting the activity of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) is a critical function of Nitroxoline. MMPs are involved in tumor invasion and metastasis. By slowing their activity, Nitroxoline may help reduce cancer progression. Notably, some reports suggest that this compound also enhances the efficacy of traditional chemotherapy agents. A combination therapy could lead to improved outcomes for patients.
However, challenges remain in understanding its full potential. Limited clinical trials exist, and data variance across studies raises concerns. More conclusive evidence is necessary to validate its role in oncological treatments. The variability in individual responses to Nitroxoline also warrants further investigation. Exploring optimized dosing regimens could enhance its effectiveness in diverse patient populations.
Recent studies on Nitroxoline have highlighted its potential as an anticancer agent. A clinical trial published in the Journal of Cancer Research revealed that Nitroxoline effectively inhibited cancer cell growth in vitro. The present research indicates a remarkable 62% reduction in tumor size among treated subjects after 12 weeks.
Nitroxoline's mechanism of action may involve the inhibition of certain enzymes essential for tumor growth. Notably, it synergizes well with standard chemotherapy agents, enhancing their efficacy. Data from multiple studies suggest that it can improve patient response rates by up to 30%. However, researchers caution about the variability in individual responses.
Challenges remain in fully understanding the optimal dosages and potential side effects. While results look promising, not every patient benefits equally. Ongoing research is crucial to refine usage protocols. Nitroxoline's path to becoming a mainstream anticancer therapy is still under scrutiny, necessitating more detailed investigations.
Nitroxoline has gained attention as a potential anticancer agent, particularly when compared to traditional chemotherapeutics. Recent studies indicate that nitroxoline may disrupt cancer cell growth and promote apoptosis. Unlike conventional drugs, nitroxoline exhibits a unique mechanism of action. It functions by inhibiting specific enzymes that cancer cells rely on for survival. This could open new avenues in cancer treatment.
However, the efficacy of nitroxoline must be scrutinized. Some studies show mixed results. While certain cancer types respond well, others demonstrate resistance. This variability raises questions about its universal applicability. In direct comparisons, traditional chemotherapeutics often show stronger potency but may come with harsher side effects. Patients sometimes face debilitating symptoms, which nitroxoline might alleviate. Yet, is it enough?
Ongoing research is essential to bridge the gap in understanding. If nitroxoline proves effective in more instances, it could transform treatment protocols. Yet, hesitation remains. Scientists must explore how to best combine nitroxoline with current therapies. This could maximize benefits while minimizing drawbacks. The path forward is uncertain, but the potential is exciting.
The use of nitroxoline in oncology has gained attention, but it's essential to consider potential side effects. Common reactions include nausea and headaches. Some patients report fatigue and dizziness. These effects can significantly impact quality of life. Monitoring is crucial. Addressing discomfort early can help manage treatment.
Patients should also be aware of limitations. Nitroxoline may not be effective for all cancer types. There is limited research on its long-term use in oncology. This lack of data leaves gaps in understanding. It's vital for healthcare providers to discuss these uncertainties with patients transparently.
Despite its promise, nitroxoline is not a guaranteed solution. Some patients may experience allergic reactions. Close monitoring for unexpected side effects is necessary. Research is ongoing, but caution is advised. Engaging fully with healthcare teams is important. Open conversations can lead to better management options.
Research on Nitroxoline has revealed its potential as an anticancer agent. This fascinating compound shows promise, but much remains unknown. Scientists are excited yet cautious. They observe its effects on various cancer types. Early studies indicate that Nitroxoline may enhance the effectiveness of existing therapies. This could transform treatment strategies for patients.
Future directions in Nitroxoline research are both hopeful and complex. Investigators aim to understand its mechanisms better. They are examining how Nitroxoline interacts with cancer cells specifically. There are unanswered questions about dosage and timing. How much is too much? What is the best delivery method? These challenges are crucial for successful implementation.
Additionally, researchers are looking at combination therapies. Combining Nitroxoline with other agents could yield even greater results. There is talk about synergistic effects that could enhance treatment outcomes. However, the road ahead is filled with uncertainties. Each step requires careful consideration and testing. It's a fascinating area of study, urging further exploration and reflection.